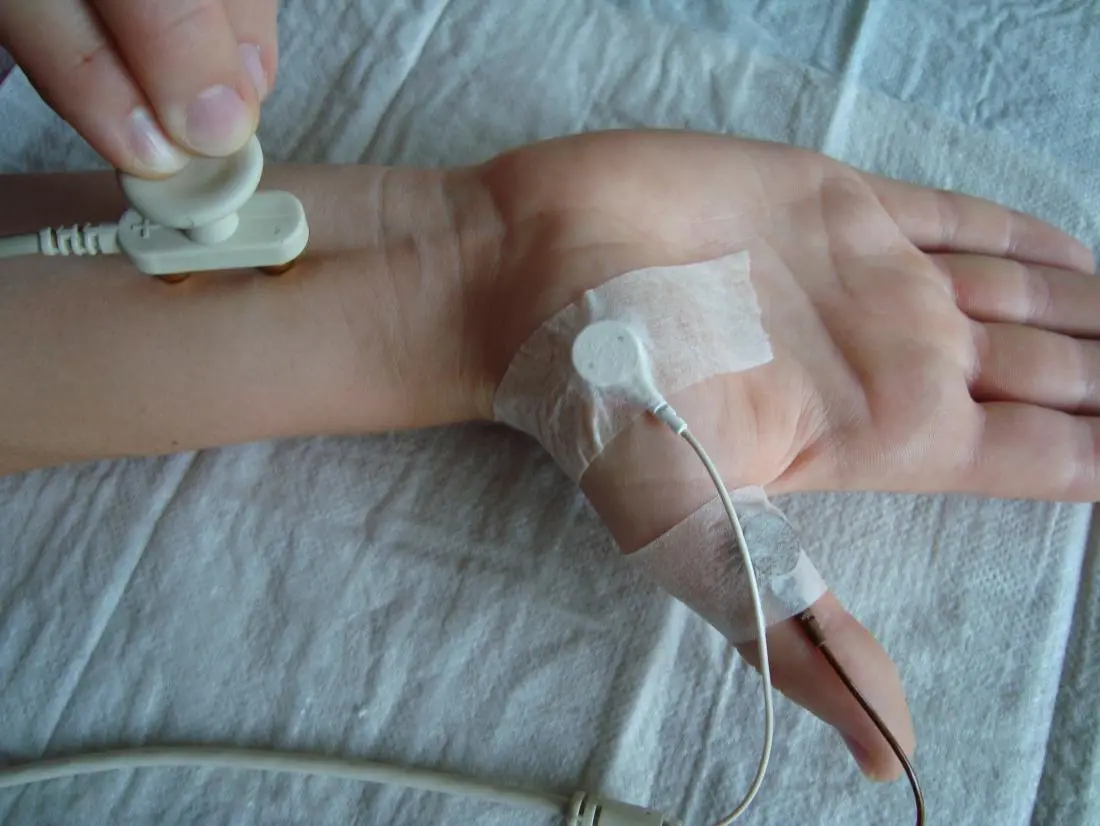
NCV & EMG
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) testing and electromyography (EMG) are diagnostic procedures commonly used in neurology to evaluate the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. These tests provide valuable information about the health of nerves and muscles, helping healthcare professionals diagnose and manage various neurological and neuromuscular disorders.NCV and EMG are valuable diagnostic tools in neurology, aiding in the evaluation of peripheral nerve and muscle function. These tests provide essential information for diagnosing conditions such as neuropathies, radiculopathies, myopathies, and other neuromuscular disorders. NCV is often used along with an EMG to tell the difference between a nerve disorder and a muscle disorder. NCV detects a problem with the nerve, whereas an EMG detects whether the muscle is working properly in response to the nerve's stimulus.
NCV measures the speed at which electrical impulses travel along a nerve. This test helps assess the integrity of the peripheral nerves and identify any abnormalities, such as nerve damage or compression. Electrodes are placed on the skin over the nerve being tested. The response, or the electrical activity generated by the nerve, is recorded by electrodes placed further along the nerve. The time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel between the two sets of electrodes is measured to calculate the nerve conduction velocity. Diagnosing peripheral neuropathies (nerve disorders). Identifying nerve damage or compression. Assessing the severity and location of nerve injuries.
EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles and the corresponding nerve pathways. This test helps assess the health and function of muscles and the nerves controlling them. A small, thin needle electrode is inserted into a muscle under examination. The electrical activity produced by the muscle at rest and during contraction is recorded. The recorded signals help evaluate the health of the muscle and the nerves supplying it. Diagnosing neuromuscular disorders. Identifying the cause of muscle weakness, twitching, or pain. Assessing the extent of nerve damage or dysfunction. Both NCV and EMG are often performed together to provide a comprehensive assessment of the peripheral nervous system and muscles. These tests can help differentiate between nerve and muscle disorders, identify the location and severity of abnormalities, and guide appropriate treatment strategies.